Publications
Publication Highlights
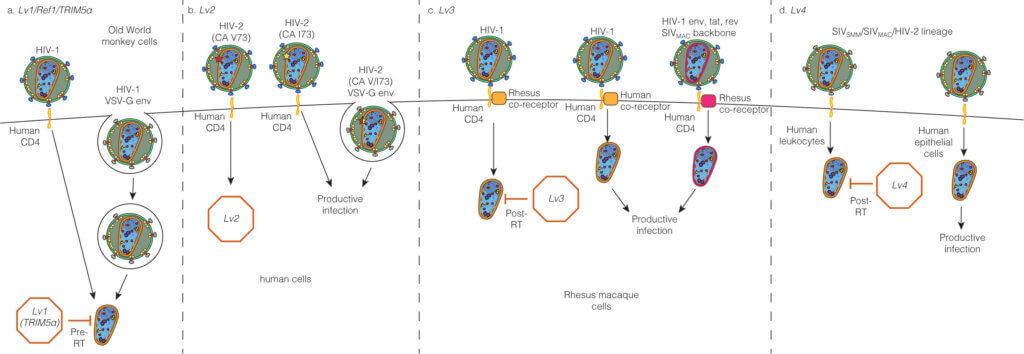
Capsid-dependent lentiviral restrictions
Twentyman, Emerman, Ohainle
We review important features of known capsid-targeting blocks to lentiviral infection together with several blocks to infection for which the genes responsible for the inhibition remain to be identified.
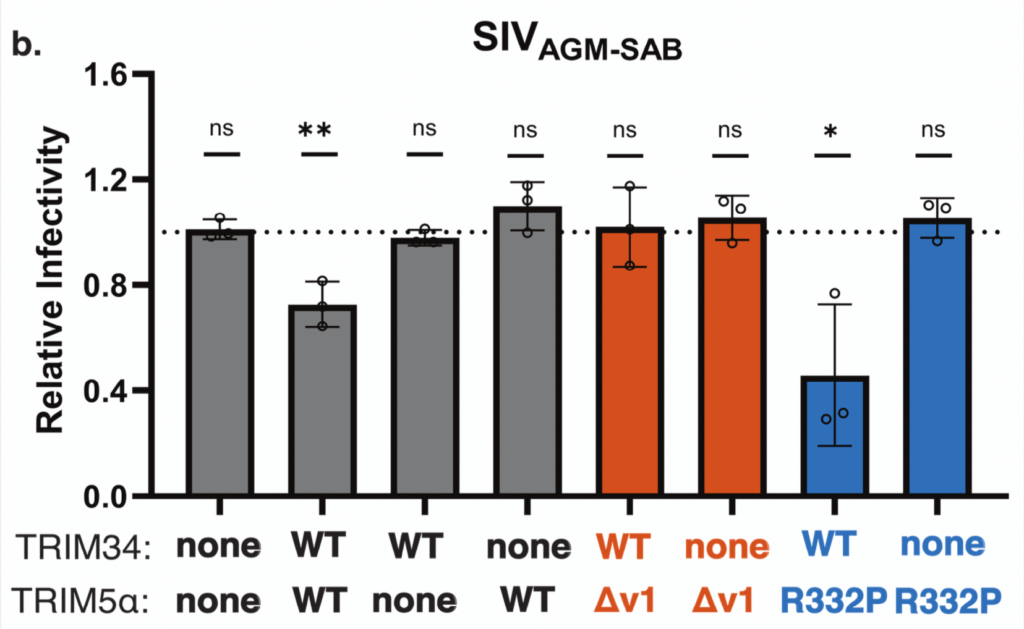
Primate TRIM34 is a broadly-acting, TRIM5-dependent lentiviral restriction factor
Twentyman, Khalifeh, Felton, Emerman, Ohainle
UW Ph.D. student Joy Twentyman demonstrates that the antiviral activity and TRIM5-dependence of TRIM34 are broadly conserved features of this antiviral gene in primates.
A Virus-Packageable CRISPR System Identifies Host Dependency Factors Co-Opted by Multiple HIV-1 Strains
MBIO 2023
Montoya, Ready, Felton, Fine, OhAinle, Emerman
This work lead by UW Ph.D. student Vanessa Montoya identifies many host cell factors that are required for efficient infection of human cells by multiple HIV strains.
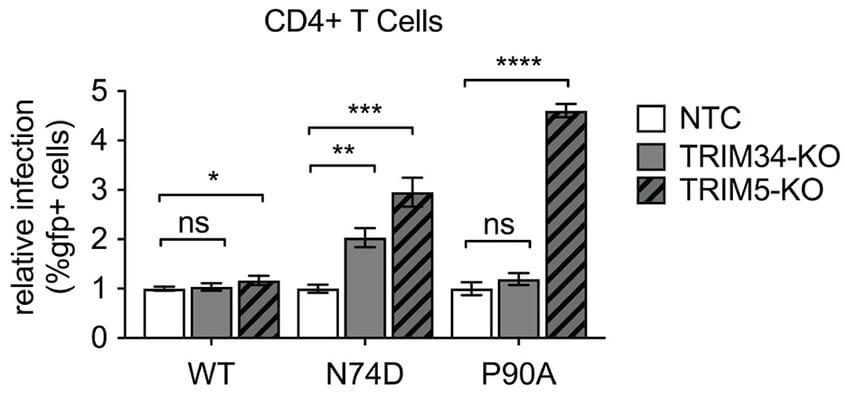
TRIM34 restricts HIV-1 and SIV capsids in a TRIM5α-dependent manner
PLoS Pathogens 2020
Ohainle, Kim, Komurlu Keceli, Felton, Campbell, Luban, Emerman
Here we identify a new retroviral restriction factor, TRIM34. We find this through screening some HIV viruses with mutations in the viral capsid protein. Intriguingly we find that TRIM34 requires its close paralog TRIM5 to also be present for efficient restriction.
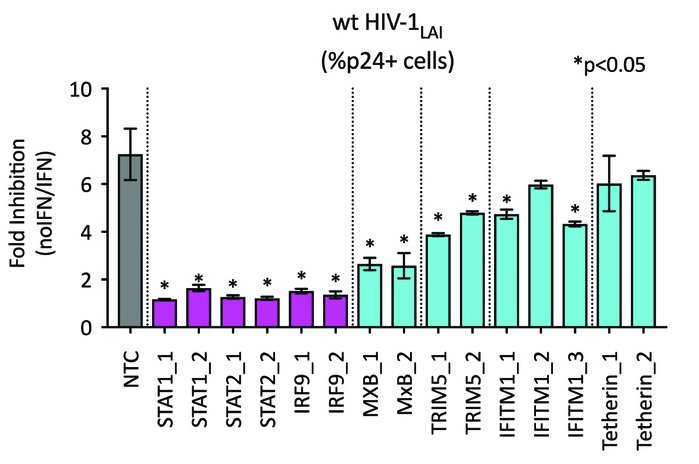
A virus-packageable CRISPR screen identifies host factors mediating interferon inhibition of HIV
eLife 2018
Ohainle, Helms, Vermeire, Roesch, Humes, Basom, Delrow, Overbaugh, Emerman
In this work we describe a new method to identify host factors that inhibit or enable HIV infection in human cells. HIV-CRISPR Screening is born!
Publications
Twentyman J, Emerman M, Ohainle M. Capsid-dependent lentiviral restrictionsJournal of Virology. 2024
Fernandes AP, Ohainle M, Esteves PJ. Patterns of evolution of TRIM genes highlight the evolutionary plasticity of antiviral effectors in mammals. Genome Biology and Evolution. 2023 (preprint:biorxiv).
Twentyman J, Khalifeh A, Felton A, Emerman M, OhAinle M. Primate TRIM34 is a broadly-conserved, TRIM5-dependent lentiviral restriction factor. Retrovirology 2023 (preprint:biorxiv).
Hsieh E, Janssens DH, Paddison PJ, Browne EP, Henikoff S, OhAinle M, et al. A modular CRISPR screen identifies individual and combination pathways contributing to HIV-1 latency. PLoS Pathogens. 2023.
Montoya VR, Ready TM, Felton A, Fine SR, OhAinle M, Emerman M. A Virus-Packageable CRISPR System Identifies Host Dependency Factors Co-Opted By Multiple HIV-1 Strains. mBio. 2023.
PDF Mac Kain A, Maarifi G, Aicher S-M, Arhel N, Baidaliuk A, Munier S, et al. Identification of DAXX as a restriction factor of SARS-CoV-2 through a CRISPR/Cas9 screen. Nat Commun. 2022;13: 2442. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-30134-9
Ohainle M, Malik HS. A balancing act between primate lentiviruses and their receptor Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118.
Roesch F, OhAinle M. HIV-CRISPR: A CRISPR/Cas9 Screening Method to Identify Genes Affecting HIV Replication. Bio Protoc. 2020;10: e3614. doi:10.21769/BioProtoc.3614
Ohainle M, Kim K, Komurlu Keceli S, Felton A, Campbell E, Luban J, et al. TRIM34 restricts HIV-1 and SIV capsids in a TRIM5α-dependent manner. PLoS Pathog. 2020;16: e1008507. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1008507
Sharma A, McLaughlin RN Jr, Basom RS, Kikawa C, OhAinle M, Yount JS, et al. Macaque interferon-induced transmembrane proteins limit replication of SHIV strains in an Envelope-dependent manner. PLoS Pathog. 2019;15: e1007925. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1007925
OhAinle M, Helms L, Vermeire J, Roesch F, Humes D, Basom R, et al. A virus-packageable CRISPR screen identifies host factors mediating interferon inhibition of HIV. Elife. 2018;7. doi:10.7554/eLife.39823
OhAinle M, Balmaseda A, Macalalad AR, Tellez Y, Zody MC, Saborío S, et al. Dynamics of dengue disease severity determined by the interplay between viral genetics and serotype-specific immunity. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3: 114ra128. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3003084
OhAinle M, Kerns JA, Li MMH, Malik HS, Emerman M. Antiretroelement activity of APOBEC3H was lost twice in recent human evolution. Cell Host Microbe. 2008;4: 249–259. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2008.07.005
OhAinle M, Kerns JA, Malik HS, Emerman M. Adaptive evolution and antiviral activity of the conserved mammalian cytidine deaminase APOBEC3H. J Virol. 2006;80: 3853–3862. doi:10.1128/JVI.80.8.3853-3862.2006
ALL PUBLICATIONS
See Our Full Citation List over on PubMed


